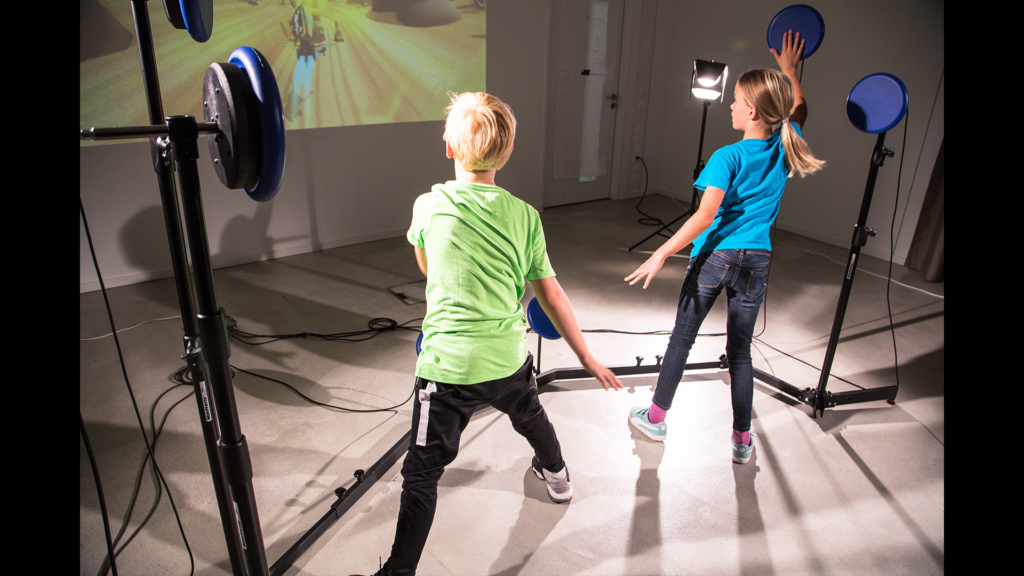
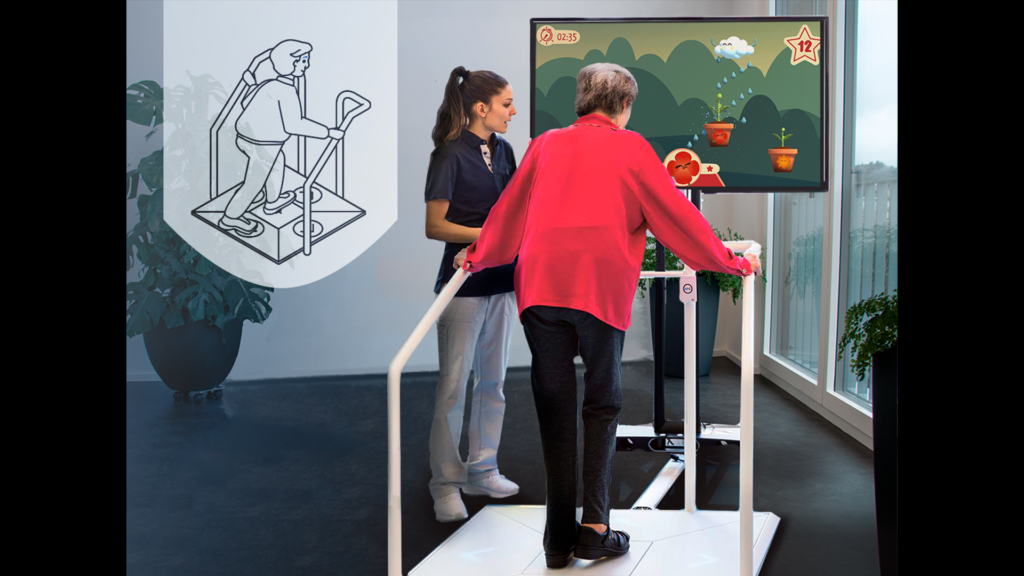
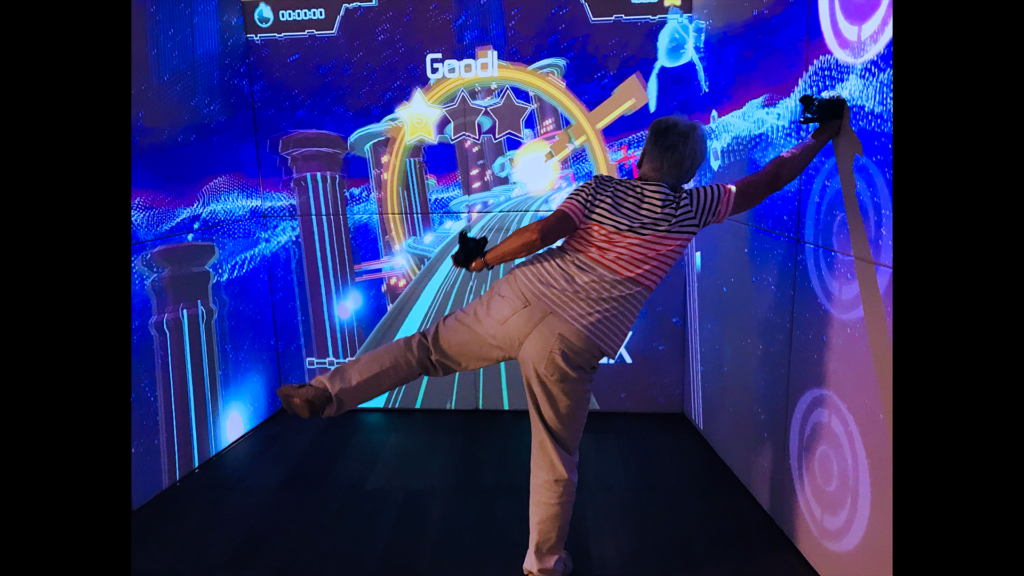
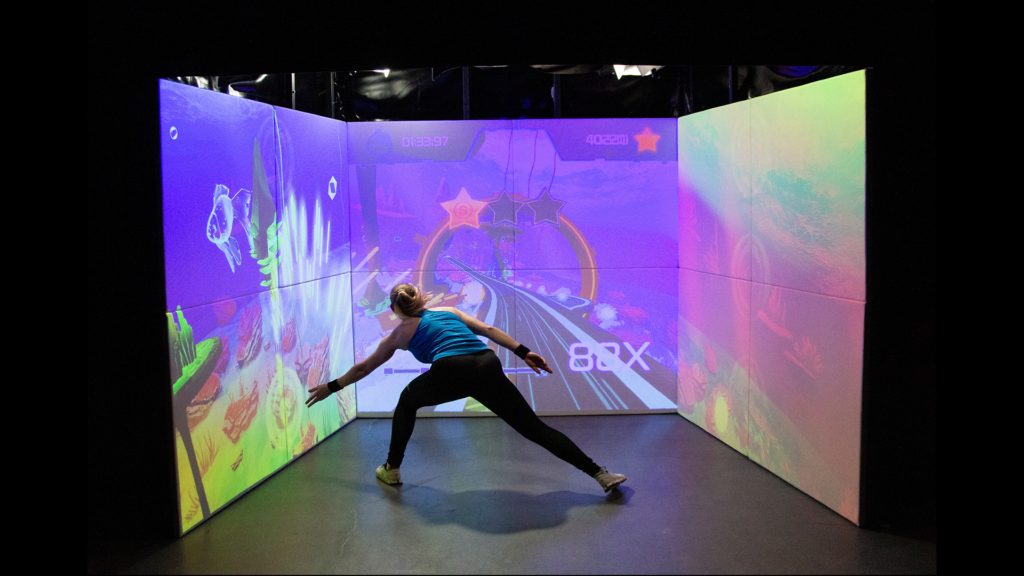
My R&D work always follows an interdisciplinary, user-centered, needs-oriented, and often participatory R&D approach. Following, you find a selection of third-party funded R&D projects I initiated, acquired, managed, and implemented.
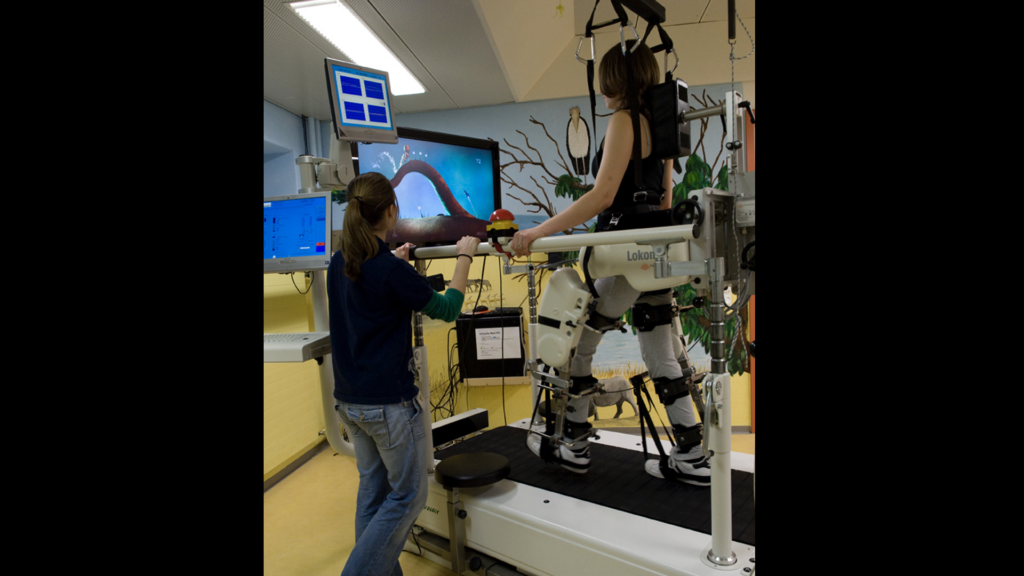
«IMIC» (Innovative Movement Therapies in Childhood) is a translational research and development project that focuses on creating a motivating and therefore more effective locomotion rehabilitation-setting for children with neurological disorders and cognitive limitations in an interdisciplinary context. The project’s main target is the expansion of pediatric robot-assisted rehabilitation of lower and upper extremities by using specifically designed RehabGames.
The project aimed to explore the user-centered design and evaluation of psychophysiological adaptive fitness game environments for children and young adolescents. We explore the potential of specifically developed exergame scenarios and full-body-motion-controller setups as motivating and effective fitness training method.
In this interdisciplinary project, the project partners target the field of neurorehabilitation with a playful cognitive-motor training by the development of user-centered exergames which were evaluated regarding their effects on cognitive and motor functions in multiple sclerosis patients.
The ExerGetic project aims to develop and examine an innovative digital training/therapy solution to individually improve physical and cognitive functions of the geriatric population. The ExerG solution is a user-centered video game-based physical exercise, a so-called exergame, providing an ecologically valid and safe training/therapy setting for the geriatric population. The ExerG solution is developed with concepts of modularity and extensibility to accommodate different usage scenarios, depending on the identified needs and business cases.
In this project, the focus is on advancing the ExerCube for sports rehabilitation. It will allow safe and motivating trainings of physical and cognitive aspects and ameliorate the return to sport of injured athletes. The efficacy of the new training regimen and use user-centered design principles to improve implementation will be evaluated.
Publications
Conference Papers and Contributions
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Riederer, Y., Ketlehut, S. & Schättin, A. (2022). Vergleich akuter Effekte verschiedener Trainingsbedingungen auf kognitive Fähigkeiten und Tapping-Leistung bei E-Sportlern. dvs Hochschultag 2022, dvs Band 298 © Edition Czwalina.
- Pickles, J., Schättin, A., Flagmeier, D., Schärer, B., Riederer, Y., Niedecken, S., Villiger, S., Jurt, R., Kind, N., Scott, S., Stettler, C. & Martin-Niedecken, A.L. Martin-Niedecken (2022). Exergaming mit „On-Body“ Feedbacksystem für den Heimgebrauch. dvs Hochschultag 2022, dvs Band 298 © Edition Czwalina.
- Nigg, C, Kubica, C, Bodman, A., Martin-Niedecken, A.L. & Ketelhut, S. (2022). Sind E-Sportler*innen wirklich so unfit und ungesund?. dvs Hochschultag 2022, dvs Band 298 © Edition Czwalina.
- Ketelhut, S., Nigg, C. & Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2022). E-Sport – Risiko oder Chance für Gesundheit, Gesellschaft, Sport und Wissenschaft. dvs Hochschultag 2022, dvs Band 298 © Edition Czwalina.
- Ketelhut, K., Röglin, L., Martin-Niedecken, A.L. & Ketelhut, S. (2022). Auswirkungen einer schulbasierten Exergaming – Intervention auf die motorische Leistungsfähigkeit. dvs Hochschultag 2022, dvs Band 298 © Edition Czwalina.
- Ketelhut, S. , Bodman, A., Kubica, C., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., and Nigg, C.R. (2021). Health Status In Competitive E-sports Athletes- A Cross Sectional Study. ERN Conference 2021.
- Nigg, C.R., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Bodman, A., Kubica, C., Zimmermann, P. Schmidt, M., and Ketelhut, S. (2021). Rationale and Perspective of the eSports Health And PErformance Network. ERN Conference 2021.
- Kriglstein, S., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Turmo Vidal, L., Klarkowski, M., Rogers, K., Turkay, S., Seif El-Nasr, M., Marquez Segura, E., Drachen, A., and Perttu Hämäläinen (2021). The Present and Future of eSports in HCI. ACM CHI 2021.
- Márquez Segura, E., Rogers, K., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Niedecken, S., Turmo Vidal, L. (2021) Exploring the Design Space of Immersive Social Fitness Games: The ImSoFit Games Model. ACM CHI 2021.
- Hug, D., Papetti, S. Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Rogers, K. and Graf, E. (2021). Sound Design for Exergames – A design research pilot project, Research Symposium of Zurich University of the Arts.
- Ketelhut, S. , Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Kircher, E., Röglin, L., Ketelhut, R.G., Hottenrott, K., Ketelhut, K. (2020). Evaluating the exercise intensity during an exergame session in the ExerCube. ECSS Congress Sevilla 2020. Sevilla, ESP.
- Patibanda, R., Semertzidis, N., Scary, M., La Delfa, J., Andres, J., Baytaş, M.A., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., et al. (2020). Motor Memory in CHI, In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. ACM.
- Zwingmann, K., Martin-Niedecken, A. L., Schättin, A. and Voelcker-Rehage, C. (2020). Short physical-cognitive (work) breaks to improve cognitive flexibility via exergaming. ECSS Congress Sevilla 2020. Sevilla, ESP.
- Martin-Niedecken A.L., Márquez Segura E., Rogers K., Niedecken, S., and Turmo Vidal L. (2019). Towards Socially Immersive Fitness Games: An Exploratory Evaluation Through Embodied Sketching. In Proceedings of the Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play Companion Extended Abstracts (pp. 525-534). ACM.
- Martin-Niedecken A.L., Rogers K., Turmo Vidal L., Mekler E. D., and Márquez Segura E. (2019). ExerCube vs. Personal Trainer: Evaluating a Holistic, Immersive, and Adaptive Fitness Game Setup. In ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems Proceedings (CHI 2019), ACM, New York, NY, USA.
- Kocher, M., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Li, Y., Kinzelbach, W., Wang, H., Bauer, R. and Lunin, L. (2019). “Save the Water” – A China Water Management Game Project. In Proceedings of the 3rd International GamiFIN Conference, GamiFIN 2019. pp. 1-12, Springer.
- Schmidt, M., Benzing, V., Bonadimann, P., Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2019). Kognitiv-anspruchsvolle sportliche Aktivität und kognitive Leistung: Profitieren denkfaule Menschen weniger?. In: Proceedings der 11. SGS-Jahrestagung «Sport und Gehirn», Freiburg. CH.
- Schmidt, M., Benzing, V., Bonadimann, P., Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2019). Cognitively engaging physical activity and cognitive performance: Is there a dose response relationship?. In: Proceedings of Health and Active Children, Verona, ITA.
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L., & Mekler, E.D. (2018). The ExerCube: Participatory Design of an Immersive Fitness Game Environment. In Joint International Conference on Serious Games, Springer, Cham, 263-275.
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2018). Designing for Bodily Interplay: Engaging with the Adaptive Social Exertion Game “Plunder Planet”. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference on Interaction Design and Children (IDC’18), pp. 19-30.
- Kocher, M., Lunin, L., Kinzelbach, W., Bauer, R., Li, Y., Wang, H., and Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2018). Save the Water! Serious Game for Water Management in Chinese Farmers. In Proceedings of 3rd Gamification and Serious Games Symposium (GSGS’18).
- Kinzelbach, W., Li, Y., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Bauer, R., Lunin, L., Kocher, M. and Wang, H. (2018). Developing a board game for chinese farmers. In Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vol. 20, EGU2018-15336-1, EGU General Assembly 2018.
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L. & Götz, U. (2017). Go with the Dual Flow: Evaluating the Psychophysiological Adaptive Fitness Game Environment “Plunder Planet”. In Alcañiz M., Göbel S., Ma M., Fradinho Oliveira M., Baalsrud Hauge J., Marsh T. (Eds). Serious Games. JCSG 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 10622, pp. 32-43.
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2017). Exploring Spatial Experiences of Children and Young Adolescents While Playing the Dual Flow-based Fitness Game “Plunder Planet”. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Application (CHIRA ’17), pp. 218-229, SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications.
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2017). Plunder Planet – A Psychophysiologically Adaptive Fitness Game Environment for Children and Young Adolescents. In Proceedings of the 2nd Gamification & Serious Game Symposium (GSGS ’17), pp. 21-22.
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L. & Götz, U. (2016). Design and Evaluation of a dynamically adaptive Fitness Game Environment for Children and Young Adolescents. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCHI Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play (CHI PLAY ’16), pp. 205-212, ACM: New York, NY, USA.
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Bauer, R., Mauerhofer, R. & Götz, U. (2015). RehabConnex – A Middleware for the Flexible Connection of Multimodal Game Applications with Input Devices used in Movement Therapy and Physical Exercising. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and Games (CIG), pp. 496-502, IEEE Xplore Digital Library.
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2015). Computer Games – Genres, Devices und deren (Transfer-) Effekte. In Könecke, Th., Preuß, H. & Schöllhorn, W. I. (Eds.), Moving Minds – Crossing Boundaries in Sport Science. In Abstracts of the 22. dvs Hochschultags in Mainz, p. 50, Feldhaus: Edition Czwalina (Schriften der Deutschen Vereinigung für Sportwissenschaft: Band 251).
- Martin, A.L., Götz, U. & Bauer, R. (2014). Development of Task-specific RehabGame Settings for Robot-assisted Pediatric Movement Therapies. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE Consumer Electronics Society Games Media Entertainment Conference (GEM), pp. 1-4, IEEE Xplore Digital Library.
- Martin, A.L. & Kluckner, V.J. (2014). Player-centred Design Model for psychophysiological adaptive Exergame Fitness Training for Children. In Proceedings of the 4th Conference on Gaming and Playful Interaction in Healthcare, Schouten, B., Fedtke, S., Schijven, M., Vosmeer, M., Gekker, A. (Eds.), pp 105-109, Springer Fachmedien: Wiesbaden.
- Martin, A.L., Götz, U., Müller, C. & Bauer, R. (2014). “Gabarello v.1.0” and “Gabarello v.2.0”: Development of motivating rehabilitation games for robot-assisted locomotion therapy in childhood. In Proceedings of the 4th Conference on Gaming and Playful Interaction in Healthcare, Schouten, B., Fedtke, S., Schijven, M., Vosmeer, M., Gekker, A. (Eds.), pp. 101-104, Springer Fachmedien: Wiesbaden.
- Martin, A.L. (2013). Exergames: One genre, many facets – Back to the Roots. In Filip Mess, F., Gruber, M. & Woll, A. (Hrsg.), „Sportwissenschaft grenzenlos?!“ (S. 177). Abstractband des 21. dvs-Hochschultag 2013 in Konstanz. Schriften der Deutschen Vereinigung für Sportwissenschaft: Band 230. Feldhaus: Edition Czwalina.
- Martin, A.L. & Wiemeyer, J. (2012). The Impact of Different Gaming Interfaces on Spatial Experience and Spatial Presence – A Pilot Study. In St. Göbel, J. Wiemeyer, B. Urban und Müller W. (Eds.). E-Learning and Games in Training, Education, Health and Sports. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science, GameDays 2012, pp. 177-182.
- Martin, A.L. & Wiemeyer, J. (2011). Technisch vermittelte Raumerfahrungen beim Spielen digitaler Sportspiele. In Kähler, R.S. & Ziemainz, J. (Hrsg.), „Zukünftige Räume im Sport“, pp. 111-120, Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the dvs-Kommission Sport und Raum, Christian-Albrecht-Universität zu Kiel. Schriften der Deutschen Vereinigung für Sportwissenschaft: Band 230. Feldhaus: Edition Czwalina.
- Martin, A.L. (2011). Interaktionen und Wechselwirkungen zwischen Mensch, Technik und Raum beim Spielen digitaler Sportspiele. In Heinen, T., Milek, A., Hohmann T. & Raab, M. (Hrsg.), Embodiment: Wahrnehmung – Kognition – Handlung. Abstractband der Tagung der dvs-Sektion Sportmotorik vom 20.-22. Januar 2011 in Köln, Deutsche Sporthochschule Köln. pp. 90-91.
Journal Papers
- Ketelhut, S., Ketelhut, R., Kircher, E., Roeglin, L., Hottenrott, K., Martin-Niedecken, A. L., & Ketelhut, K. (2022). Gaming for better health? Comparison of cardiorespiratory and hemodynamic responses of exergaming with moderate endurance exercise. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, 29(Supplement_1), zwac056-120.
- Kriglstein, S., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Spjut, J., Damen, N.B., Turkay, S., Drachen, A. (2022) Esports Meets Human Computer Interaction. ACM Interactions, 29(3), 42-47.
- Kircher, E., Ketelhut, S., Ketelhut, K., Röglin, L., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Hottenrott, K. and Ketelhut, R.G. (2022). Acute Effects of Heart Rate-Controlled Exergaming on Vascular Function in Young Adults. Games for Health Journal Research, Development, and Clinical Applications, Volume 11, Number 1.
- Ketelhut, S., Ketelhut, R.G., Kircher, E., Röglin, L., Hottenrott, K., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., and Ketelhut, K. (2022). Gaming instead of training? Exergaming induces high-intensity exercise stimulus and reduces cardiovascular reactivity to cold pressor test. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, section Hypertension.
- Kircher, E., Ketelhut, S., Ketelhut, K., Röglin, L., Hottenrott, K., Martin-Niedecken, A. L., & Ketelhut, R. G. (2022). A Game-Based Approach to Lower Blood Pressure? Comparing Acute Hemodynamic Responses to Endurance Exercise and Exergaming: A Randomized Crossover Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1349.
- Nagel, N., Fannasch, P., Martin-Niedecken, A. L., Mühlbäck, K., Polfuß, J., & Hodeck, A. Digitales Trainingsmanagement–Eine kritische Analyse der Potentiale zur Aktivierung von Trainierenden in Fitnessstudios. Leipziger Sportwissenschaftliche Beiträge Jahrgang 63 (2022 Heft 1, 96)
- Röglin, L. Ketelhut, S., Ketelhut, K., Kircher, E., Ketelhut, R., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Hottenrott, K., and Stoll, O. (2021). Adaptive High-Intensity Exergaming – The More Enjoyable Alternative to Conventional Training Approaches Despite Working Harder. Games for Health Journal Research, Development, and Clinical Applications, Volume 10, Number 6.
- Ketelhut, S., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Zimmermann, P. and Nigg, C.R. (2021). Physical activity and health promotion in esports and gaming – discussing unique opportunities for an unprecedented cultural phenomenon. Front. Sports Act. Living – Movement Science and Sport Psychology
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Schwarz, T. and Schättin, A. (2021). Comparing the Impact of Different Heart-Rate-Based In-Game Adaptations in an Exergame-Based Functional High-Intensity Interval Training on Training Intensity and Experience in Healthy Young Adults. Front. Psychol.
- Ketelhut, S., Röglin, L., Kircher, E., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Ketelhut, R., Hottenrott, K. and Ketelhut, K. (2021). The New Way to Exercise? Evaluating an Innovative Heart-rate-controlled Exergame. International Journal of Sports Medicine 2021, 42, pp. 1–6.
- Schättin, A., Häfliger, St., Früh, B., Meyer, A., Böckler, S., Hungerbühler, Y., de Bruin, E.D., Frese, S., Steinlin Egli, R., Götz, U., Bauer, R., and Martin-Niedecken A.L. (2021). «Senso Exploria»: Design and Evaluation of User-Centered Exergames for Multiple Sclerosis Patients. JMIR Serious Games.
- Martin-Niedecken A.L., Mahrer, A., Rogers, K., De Bruin, E.D., and Schättin, A. (2020). «HIIT» the ExerCube: Comparing the Effectiveness of Functional High-Intensity Interval Training in Conventional vs. Exergame-Based Training. Frontiers in Comp. Sci.
- Martin-Niedecken A.L. and Schättin A. (2020) Let the Body’n’Brain Games Begin: Toward Innovative Training Approaches in eSports Athletes. Front. Psychol. 11:138.
- McCaskey, M.A., Schättin, A., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., and de Bruin, E.D. (2018). “Making More of IT: Enabling Intensive Motor Cognitive Rehabilitation Exercises in Geriatrics Using Information Technology Solutions,” BioMed Research International, vol. 2018, Article ID 4856146, 17 pages.
- Florian «Floyd» Mueller, Josh Andres, Joe Marshall, Dag Svanæs, m. c. schraefel, Kathrin Gerling, Jakob Tholander, Anna Lisa Martin-Niedecken, Elena Márquez Segura, Elise van den Hoven, Nicholas Graham, Kristina Höök, and Corina Sas. 2018. Body-centric computing: results from a weeklong Dagstuhl seminar in a German castle. Interactions 25, 4 (June 2018), pp. 34-39.
- Martin, A.L., Götz, U. & Bauer, R. (2014). “IMIC – Innovative Movement Therapies in Childhood”. In Neurologie & Rehabilitation, Dettmers, C., Schönle, P.W., Weiller, C. (Eds.) and Wiemeyer, J. (Guest Ed.), 20th ed., vol. 4, pp. 215-225, Hippocampus: Bad Honnef.
- Martin, A.L. & Wiemeyer, J. (2012). Technology-mediated experience of space while playing digital sports games. International Journal of Computer Science in Sport, 11 (Special Edition 1: Serious Games – Theory, Technology & Practice), pp. 135-146.
Books
- Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2021). Towards Balancing Fun and Exertion in Exergames: Exploring the Impact of Movement-Based Controller Devices, Exercise Concepts, Game Adaptivity and Player Modes on Player Experience and Training Intensity in Different Exergame Settings. PhD-Thesis. Technische Universität Darmstadt, https://tuprints.ulb.tu-darmstadt.de/id/eprint/14186
- Göbel S, Caserman P, Hansen J, Bruder R, Abels S, Behrmann M, Hauge JB, Limpach O, Reichert M, Junge J, Vogt S, Raubold O, Nowarra N, Kruse R, Roller W, Streicher A, Walter T, Wacker M, Flory C, Hugo OA, Grimm P, Dörner R, Breitlauch L, Steinicke M, Bergmeyer W, Thiele-Schwez M, Althoff US, Wunsch H, Mildner P, Hofstaetter J, Kickmeier-Rust M, Rösch A, Schmoldt D, Stock R, Tackenberg S, Katzky U, Konrad R, Wiemeyer J, Kruse L, Hobmeier G, Herkersdorf M, Kalbe E, Brach M, Müller-Lietzkow J, Unger T, Martin-Niedecken, A.L. (2018). DIN SPEC 91380:2018-06 – Serious Games Metadata Format. 1. Ed, Berlin: Beuth Verlag.
Book Chapters
- Ketelhut, S., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Kubica, C., Nigg, C (2021). Stärkung physischer Leistungsressourcen im E-Sport. In Möckel, M. (Ed.). E-Sport Training: Lehrbuch für Trainerinnen und Trainer, Academia. ISBN 978-3-89665-960-6
- Dörner, R., Martin-Niedecken, A.L., Kocher, M., Baranowski, T., Kickmeier-Rust, M., Göbel, S., Wiemeyer, J. & Gebelein, P. (2016). Contributing Disciplines. In Dörner, R., Göbel, S., Effelsberg, W. & Wiemeyer, J. (Eds.). Serious Games – Foundations, Concepts and Practice, pp. 35-55, Springerlink.